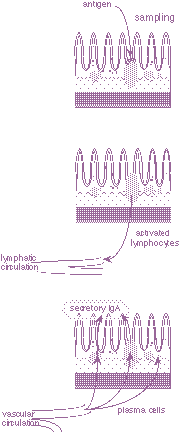
Activation of immune response
|
immune functions |
 Activation of immune response |
|
motility |
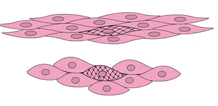 Smooth Muscle Cells, relaxed and contracted  Interstitial Cells of Cajal |
References and Advanced Reading. For an overview of motility this is recommended-but only if you have a weekend-a long weekend-without anything else pressing to do: The Motility of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Its beautifully written though-by James Christensen-and covers most of what you might ever want to know about gut motility. Starts off with "Life originated in the watery medium of the primordial seas..." [link valid April '05]. There is a lack of gastrointestinal immunology in Berne & Levy (in fact, no immune system physiology at all!). This link was down when last checked on 6th April 2005; http://www.uicomp.uic.edu/Pathology/infec11.htm but had an interesting description of lymph follicles, which form 'Peyer's patches' in the gut wall (and lymph nodes elsewhere). Suggestions for a replacement link would be appreciated. Material on GI immunity and (many other gut topics) is available at http://www.GastroAtlas.com (need to login first-this is free) but its detailed-may be more useful for looking up particular points [link valid April '05]. Slide credit; AstraZeneca for GastroAtlas "the online version of Mark Feldman's Atlas of Gastroenterology and Hepatology". |
Sample multiple-choice question for discussion. Peristalsis (choose the best answer)... a) is symmetrical in direction b) has a basal electrical rate of about 4 cycles per second c) is involuntary (proceeds without forebrain input) d) only occurs when a food bolus stretches the gut wall e) none of the above |